Respiratory Muscle Strength in Multiple Sclerosis Patients
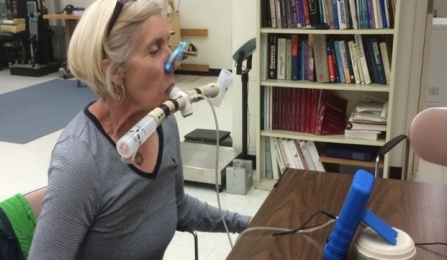
Investigators studied the effects of a resistive respiratory muscle exercise training program on respiratory muscle strength and endurance, as well as fatigue, exercise capacity, and functional performance, on Multiple Sclerosis patients.
Principal Investigators: Nadine M. Fisher, EdD, and Andrew Ray, PhD
Funding Agency: National Institute on Disability, Independent Living and Rehabilitation Research
Abstract: Fatigue, a common symptom of multiple sclerosis (MS), affects all muscles in the body, including the respiratory muscles. Respiratory muscle weakness contributes to reduced exercise capacity. It has been shown that exercise can increase strength and reduce fatigue in MS patients. Therefore, by improving the strength and endurance of the respiratory muscles of MS patients, it is likely that the exercise capacity and overall physical functioning will improve and overall fatigue will be reduced. Researchers tested a short-term resistance exercise training program for the inspiratory and expiratory muscles on patients with mild to moderate MS, using a specifically designed device. A follow-up maintenance program determined the potential for maintaining improvements using a commercially available device.

